|
I am a computer vision PhD student in the Visual Machines Group with Prof. Achuta Kadambi at UCLA. Before starting my PhD, I received my Bachelor's in Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Southern California (USC) in 2021 and worked in the GSP Lab with Prof. Antonio Ortega and the S2L2 Lab on inverse reinforcement learning with Prof. Rahul Jain. In 2020-2021, I worked at NASA JPL on TriG GPS receivers (mounted on Cosmic-2) to support tracking of GALILEO satellites. In 2025, I interned at a startup, Terrawise AI, developing computer vision models for robot navigation and solar asset monitoring as well as agentic LLM applications for robotic fleet management. vilesov@ucla.edu / (626)-390-7241 |

|
|
My current research focuses on equipping and evaluating vision-language models (VLMs) with spatial intelligence — understanding and reasoning about 3D/4D, physical relationships, and reasoning overfrom multimodal input. I am also broadly interested in topics related to large language models, diffusion models, digital health, and camera security. * indicates equal contribution |
|
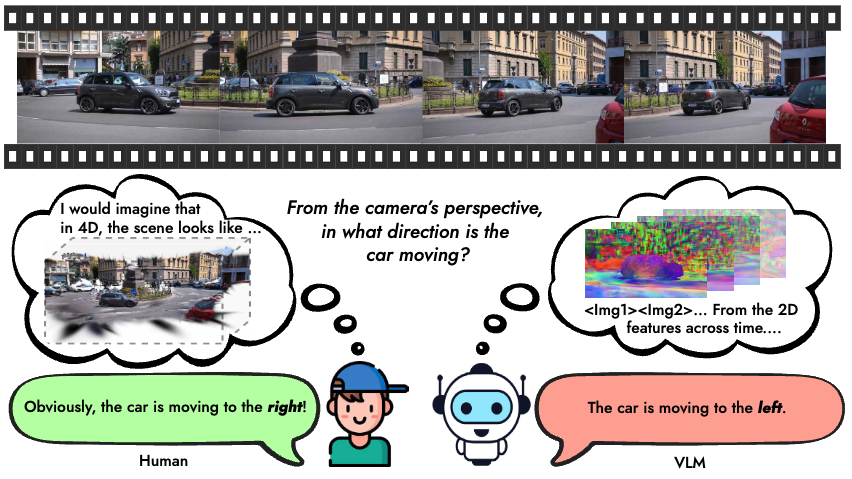
Shijie Zhou*, Alexander Vilesov*, Xuehai He, Ziyu Wan, Shuwang Zhang, Aditya Nagachandra, Di Chang, Dongdong Chen, Xin Eric Wang, Achuta Kadambi, ICCV , 2025 Project Page / Paper Link We introduce a benchmark to evaluate vision-language models on spatiotemporal reasoning in real-world and synthetic videos, revealing limited intelligence in problems that are exceedingly easy for humans. We show this through a detailed analysis of our dataset across a large set of today's top model and present preliminary methods for improving spatiotemporal intelligence. |

|
Seongbin Park*, Alexander Vilesov*, Jinghuai Zhang, Hossein Khalili, Yuan Tian, Achuta Kadambi, Nader Sehatbakhsh, to appear in 34th Usenix Security Symposium (Usenix Security) , 2025 Paper Link / Code We present Chimera, an end-to-end attack that creates cryptographically signed (e.g. C2PA) fake images capable of fooling both deepfake and image recapture detectors. The key idea is developing a two-step attack strategy where the transformation caused by image recapture can be learned and hence compensated for by a model that in turn regenerates detection-free images. |
|
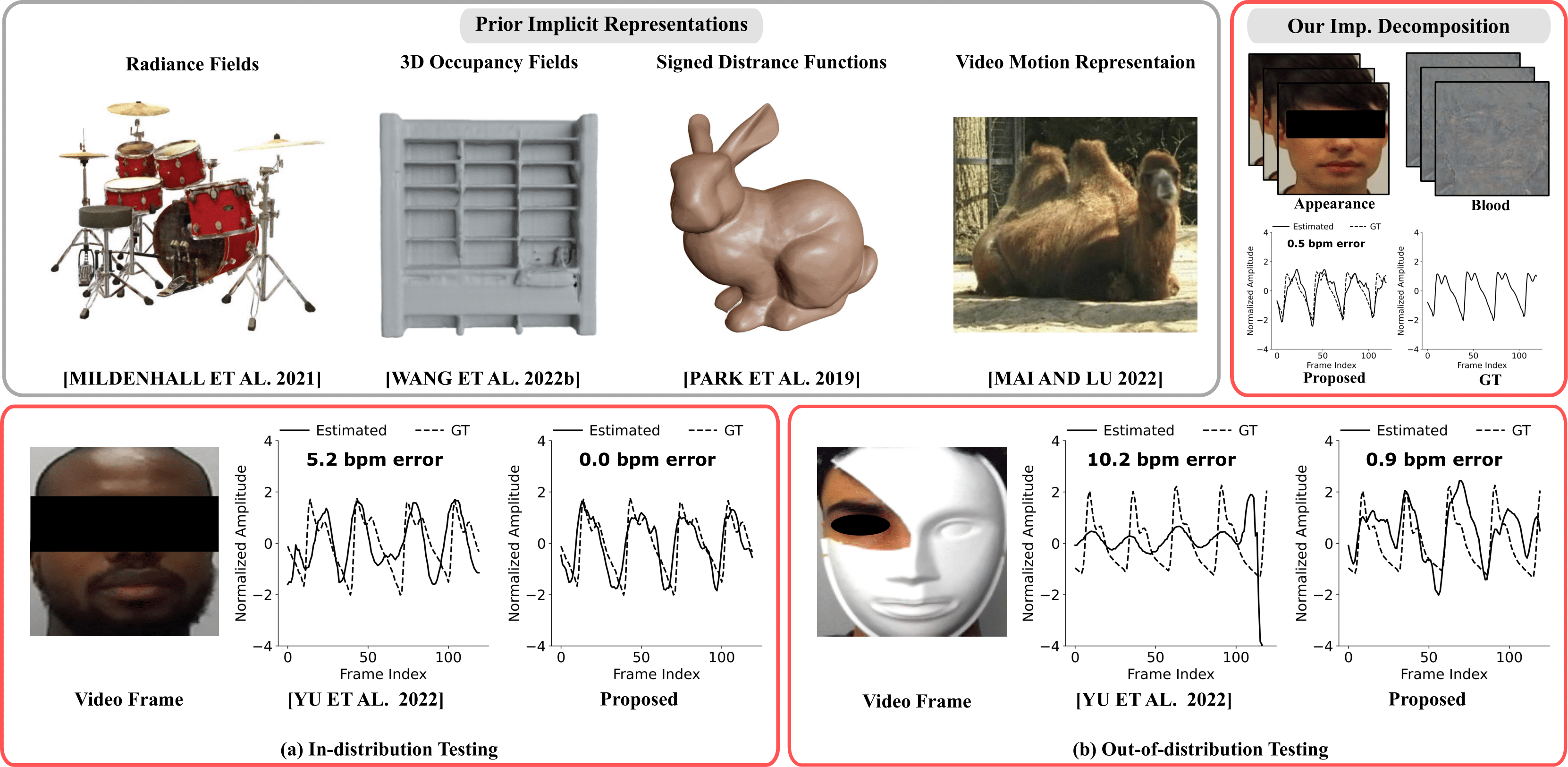
Pradyumna Chari, Anirudh B. Harish, Adnan Armouti, Alexander Vilesov, Sanjit Sarda Laleh Jalilian, Achuta Kadambi ECCV, 2024 Project Page / Paper Link / Code We propose a new implicit neural representation, that enables fast and accurate decomposition of face videos into blood and appearance components. This allows contactless estimation of heart rate from challenging out-of-distribution face videos. |

|
Alexander Vilesov, Yuan Tian, Nader Sehatbakhsh, Achuta Kadambi White Paper, 2024 Paper Link The rapid advancement of generative AI threatens the credibility of real images and videos, as synthetic content will soon be indistinguishable from camera-captured media and easily accessible to all. This white paper explores detection and cryptographic methods to reliably differentiate real images from synthetic ones, analyzing existing strategies and proposing improvements to enhance their effectiveness. |

|
Alexander Vilesov*, Pradyumna Chari*, Achuta Kadambi Arxiv, 2023 Project Page / Paper Link We present a method for 3D generation of multi-object realistic scenes from text by utilizing text-to-image diffusion models and Gaussian radiance fields. These scenes are decomposable and editable at the object level. |
|
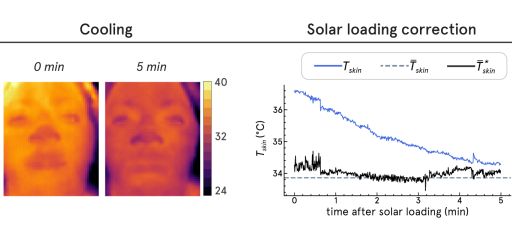
Ellin Zhao, Alexander Vilesov, Shreeram Athreya, Pradyumna Chari, Jeanette Merlos, Kendall Millett, Nia St Cyr, Laleh Jalilian, Achuta Kadambi Arxiv, 2023 Paper Link Despite the wide use of thermal sensors for temperatures screening, estimates from thermal sensors do not work well in uncontrolled scene conditions such as after sun exposure. We propose a single-shot correction scheme to eliminate solar loading bias in the time of a typical frame exposure (33ms). |
|
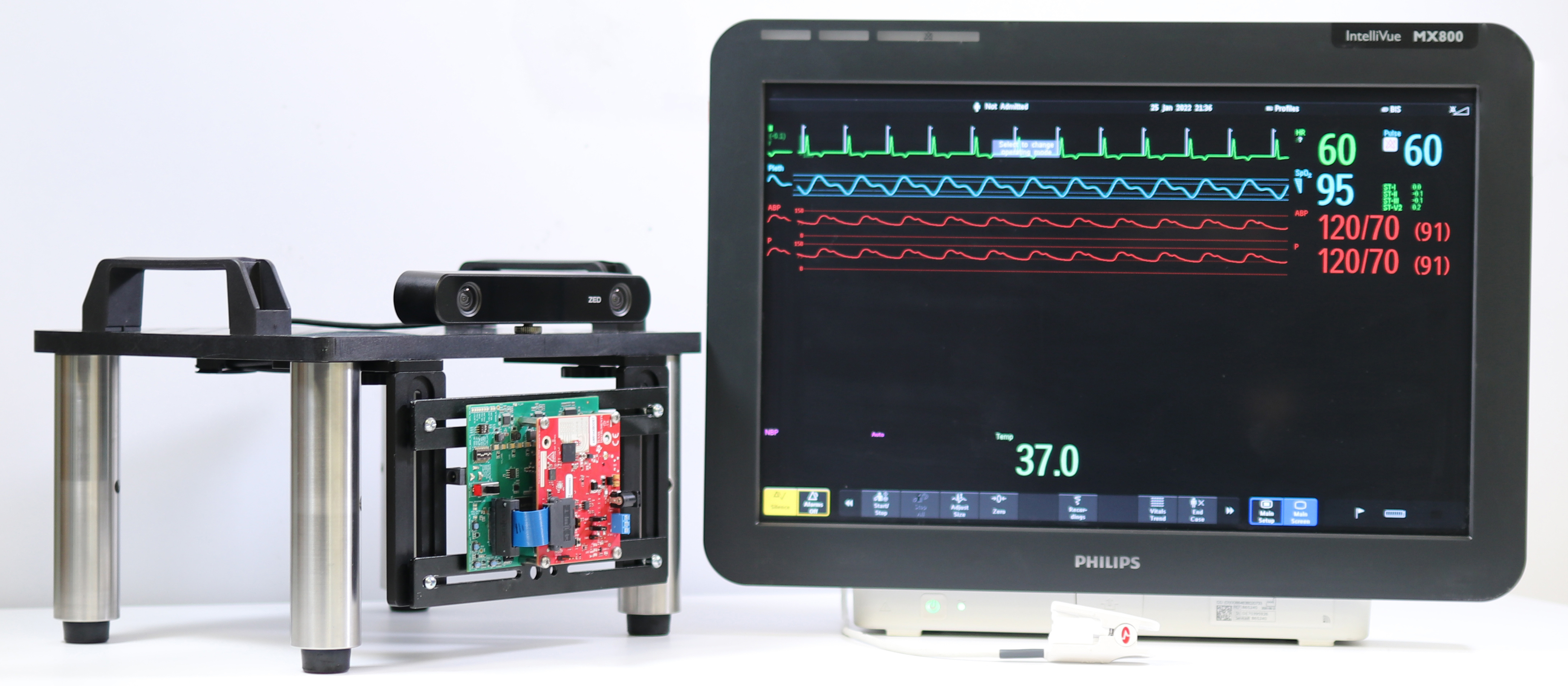
Alexander Vilesov*, Pradyumna Chari*, Adnan Armouti*, Anirudh B. Harish, Kimaya Kulkarni, Ananya Deoghare, Laleh Jalilian, Achuta Kadambi SIGGRAPH, 2022 Project Page / Paper Link / Code and Dataset To overcome fundamental skin-tone biases in camera-based remote plethysmography, we propose an adversarial learning-based fair fusion method, using a novel RGB Camera and FMCW Radar hardware setup. |